How-to Image Editing
This How-to briefly explains two ways to edit the transparency of images in Fledermaus.
On this page:
Introduction
The transparency functionality in Fledermaus is useful to show data underneath images or planes (see Figure 1a) without masking the image around the data. Another way to use transparency with images is to use the masking transparency channel, this technique makes parts of the images transparent based on the color channel chosen (see Figure 1b). For the Image Transparency example scene the Bathymetry Data used is from the Fisheries and Oceans Canada Non-Navigational Bathymetry Data, and the Geo-images used are from the New Brunswick GeoNB Data Catalog on part of the Miramichi River in N.B., Canada. For the masking transparency channel scene the raster chart is from NOAA and the data is from the Fisheries and Oceans Canada Non-Navigational Bathymetry Data in the Thunder Bay, ON, Canada area.
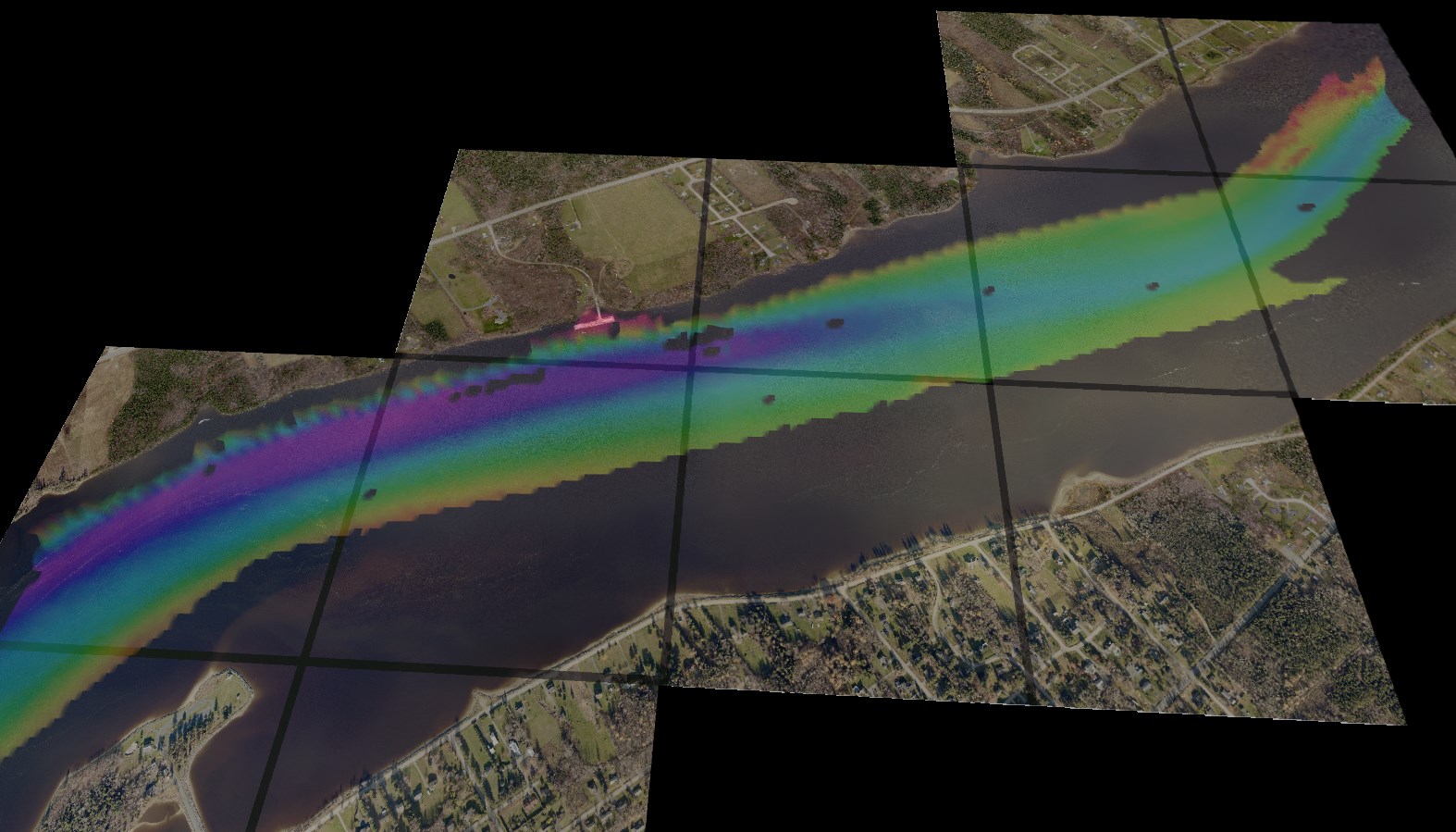
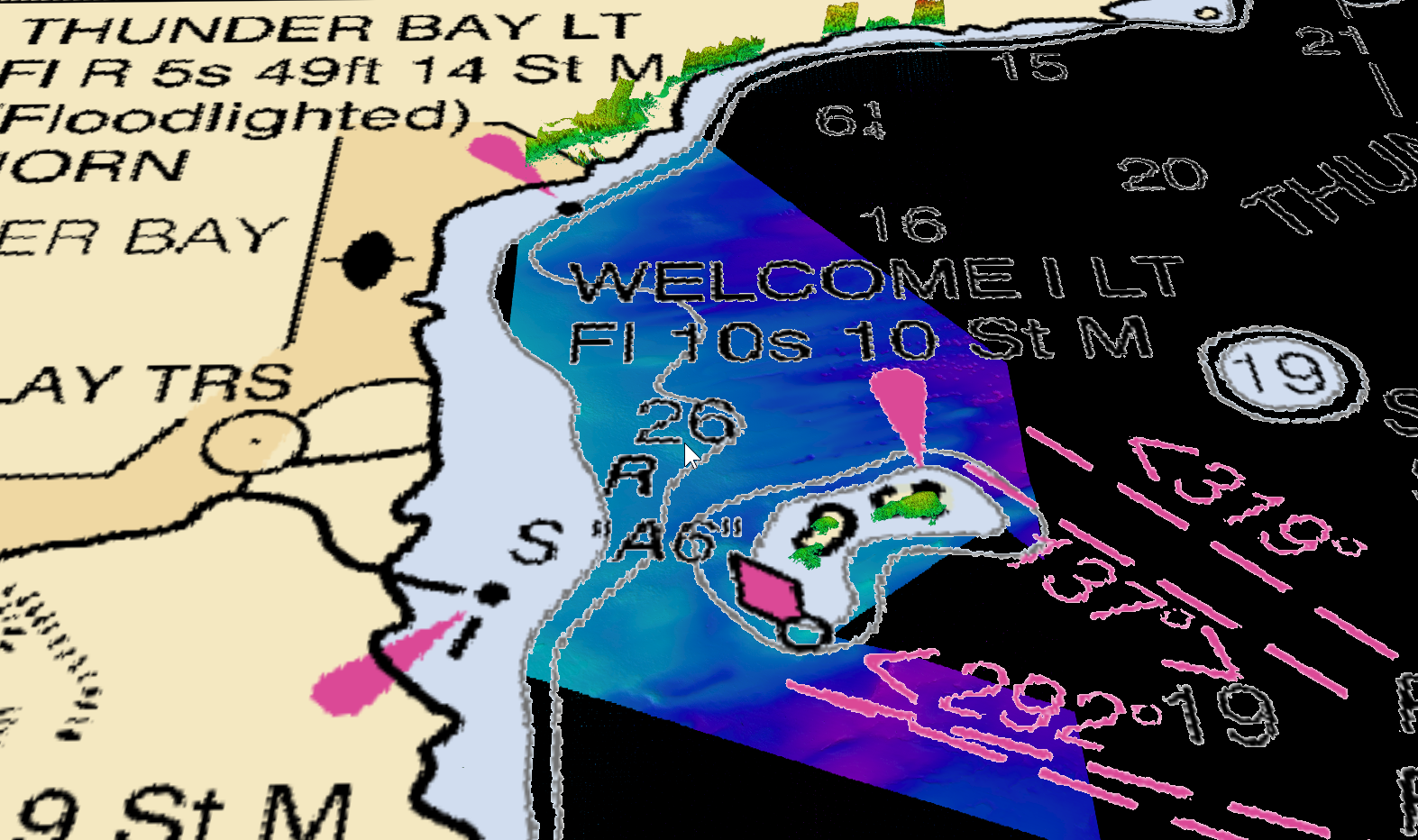
Figures 1a and b. The Image Transparency function and the Masking Transparency Channel function that can used on images to show the surface underneath.
Making an Image Transparent
Create a Fledermaus Scene with images and other data, where you would like to make the images transparent. To make an image transparent select the image in the Scene Objects dock. In the Attribute Panel, change the transparency with the slide bar or the toggle box (see Figure 2). The image transparency can be changed from 0% to 100% transparent (see Figures 3a, b, and c) depending on how much of the data needs to be seen underneath.
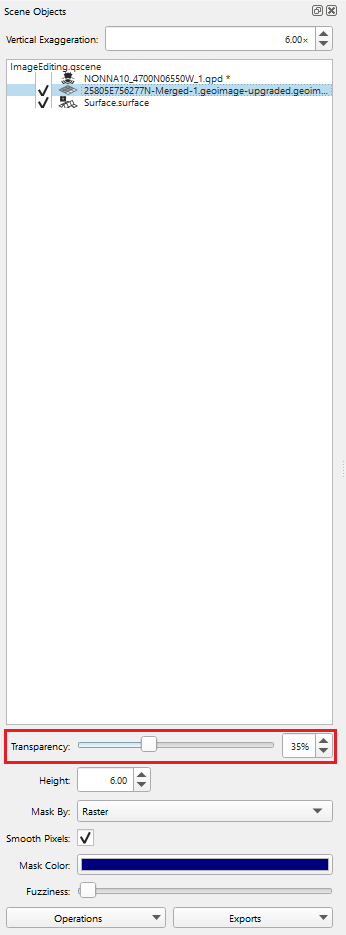
Figure 2. The red rectangle indicates where the Transparency function is in the attribute panel.
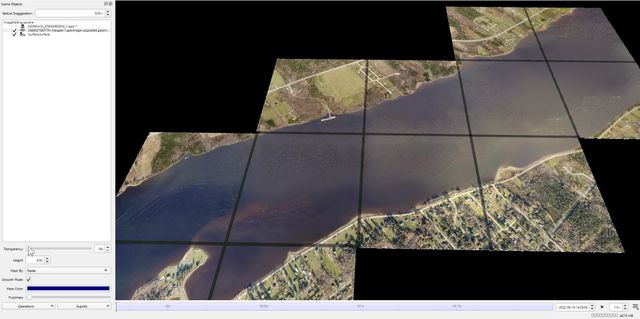
3a: Transparency 0%
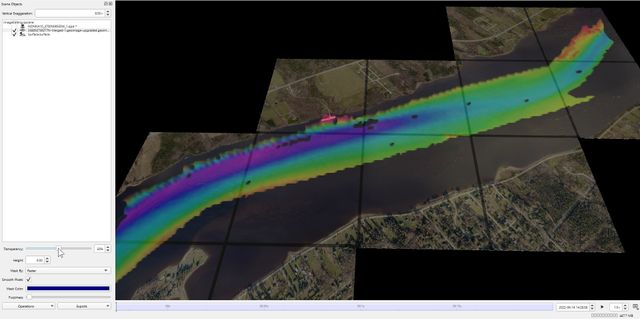
3b: Transparency 50%
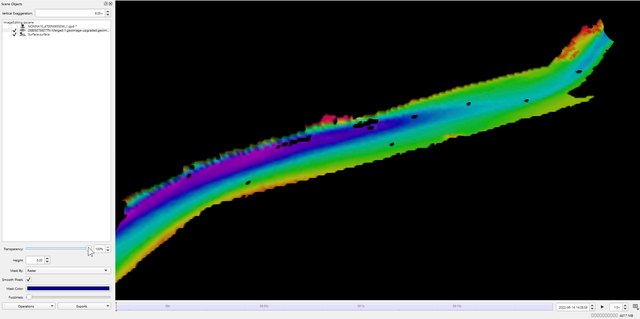
3c: Transparency 100%
Using Masking Transparency Channel to Make an Image Transparent
The Masking Transparency Channel can be used to make part of the image transparent based on the color channel chosen. To use this technique change the "Mask by" channel to color in the dropdown menu (see Figure 4). Select the "Mask Color" (see Figure 5a) to open the Select Color dialog box and choose the color you would like to make transparent in the image (see Figure 5b). Use the "Fuzziness" slide bar to change the transparency of that color channel. For some color channels, like those in Figures 6a and b, the color channel will become transparent when the "Masked by" is changed to that color. When the color is chosen in the "Mask Color" the color will disappear from the chart making it easier to see the features on a raster chart (see Figure 6c).

Figure 4. Change the "Mask by" Channel.
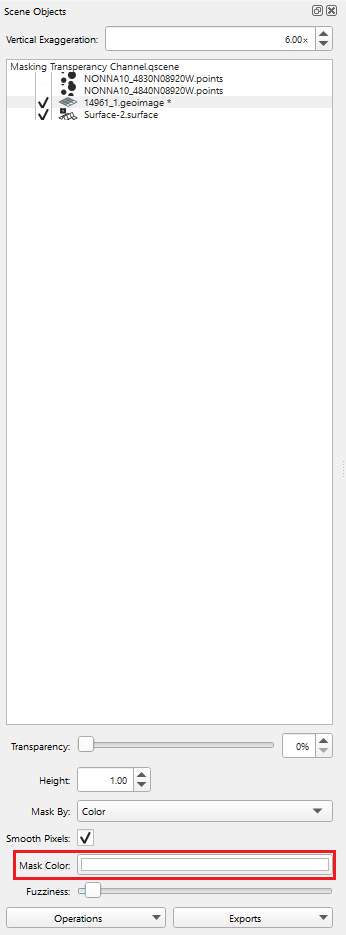
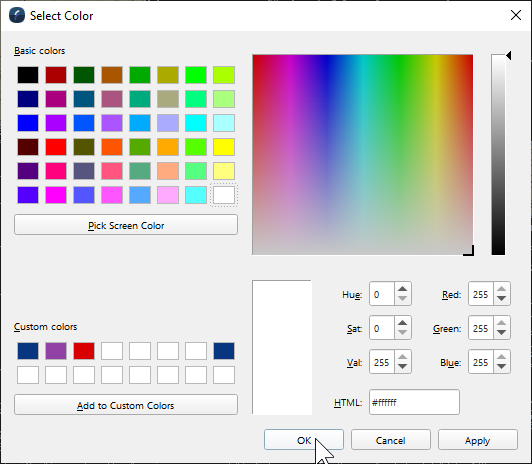
Figures 5a and b. Choose the color channel to mask.
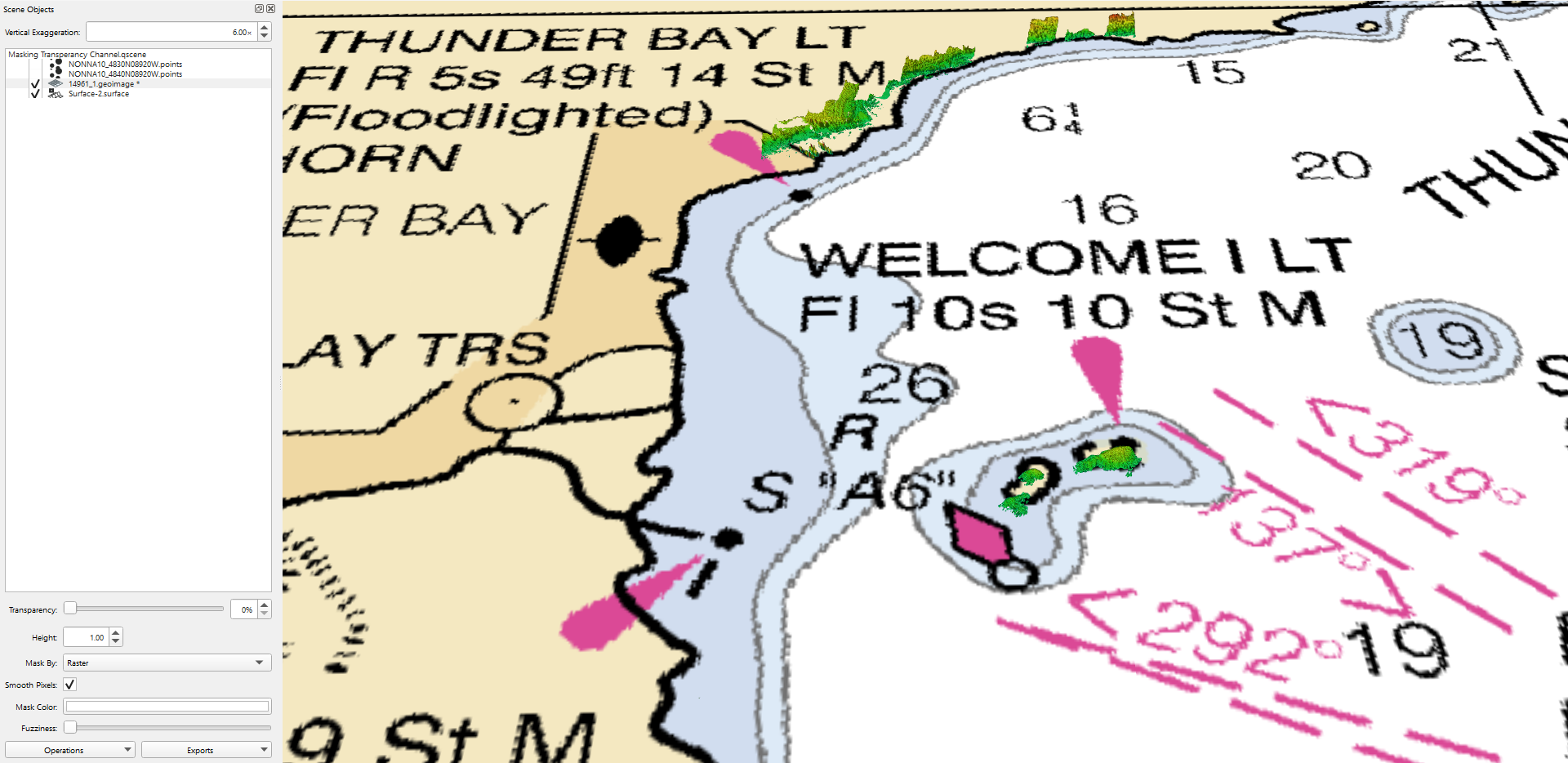
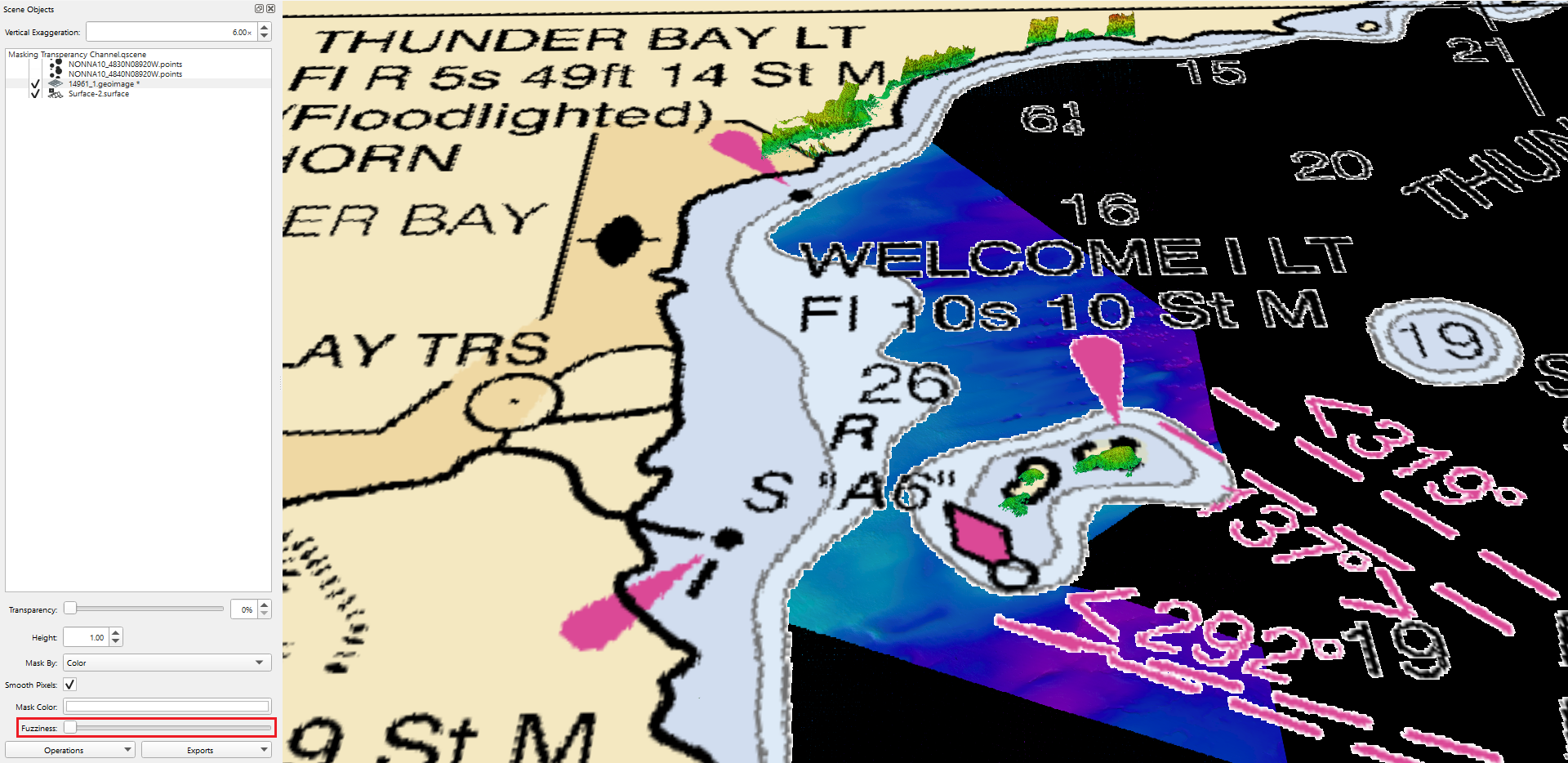
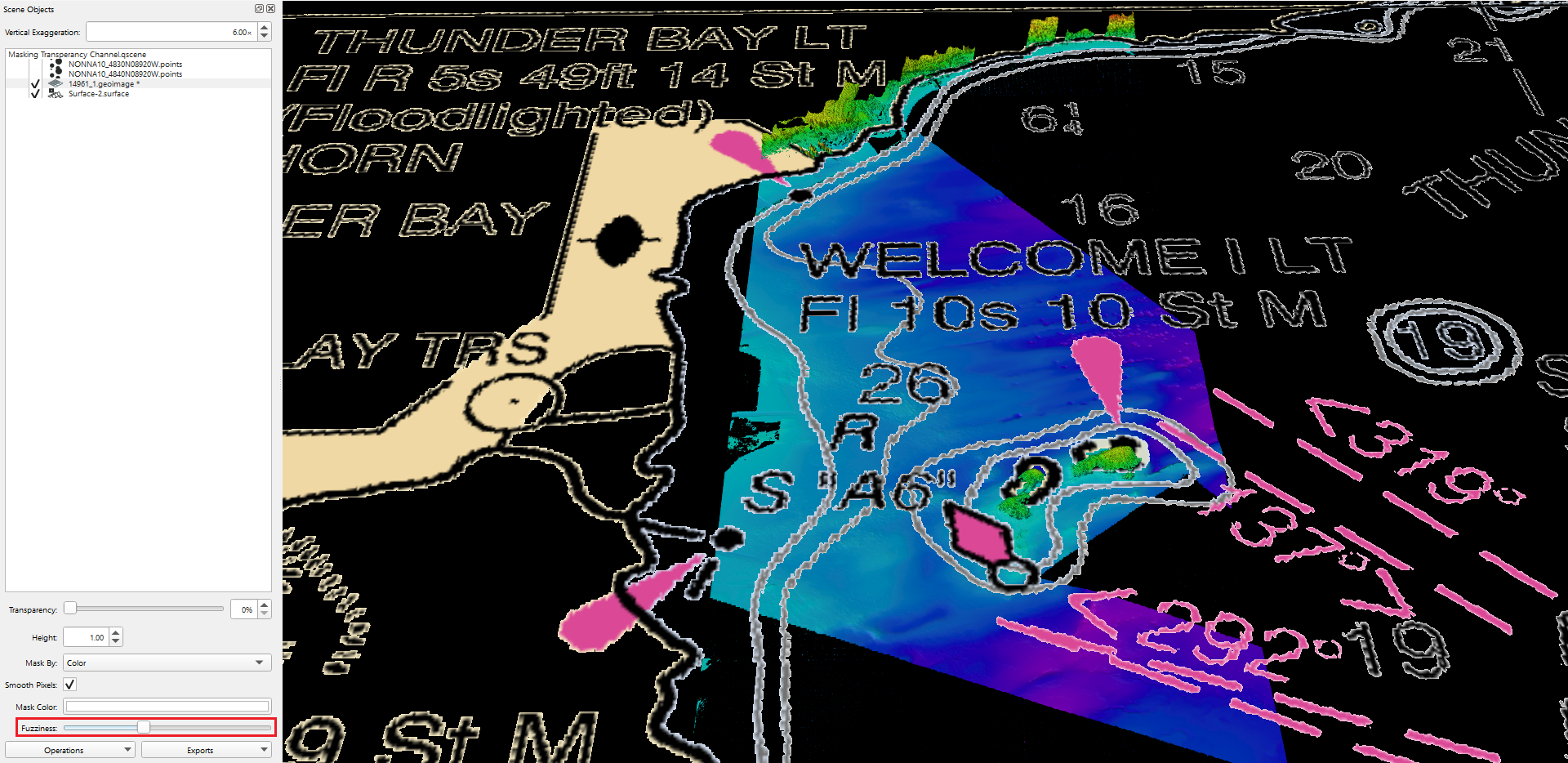
Figures 6a, b, and c. The masked transparency channel with raster and white as the color to mask by, and using the "Fuzziness" scalebar to show details.
