Qimera Cooperative Cleaning
This method allows the lead data processor or surveyor-in-charge to maintain full control of the sensor and geodetic information while farming out the data cleaning to other and/or multiple data processors.
This is done by creating sub projects from the main project, and these these sub projects have their own Dynamic Surface and QPDs to work on; there is no resource conflict between the main project and the sub projects.
Once cleaning is done in the sub projects, Qimera then seamlessly re-integrates the data back to the master project for final quality control and product creation by the lead surveyor.
The graphic below explains the basic workflow concepts.
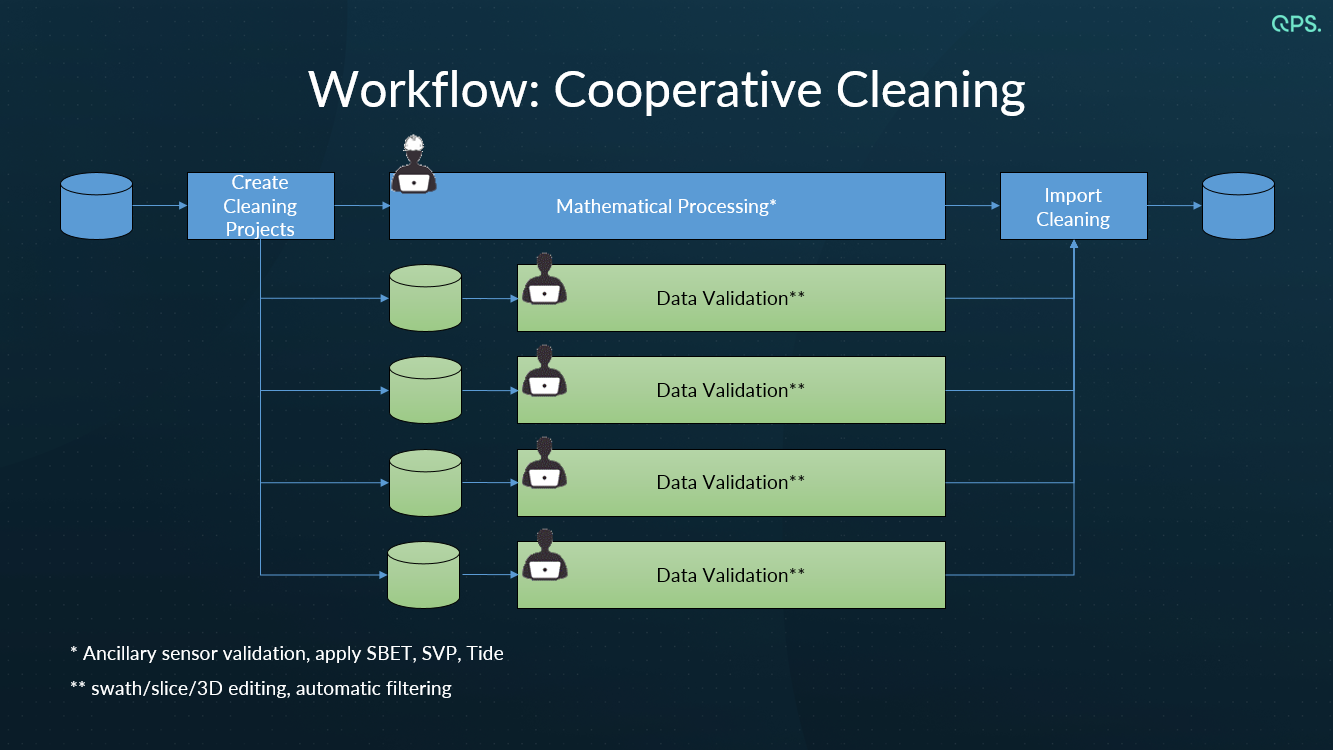
Benefits of Cooperative Cleaning:
- Multiple users can be tasked with working on the main bottleneck of multibeam sonar processing which is data cleaning, thereby rapidly reducing the time it takes to clean and validate multibeam survey data.
- All creation and re-integration of sub-projects is controlled by Qimera. There are no manual copy and paste operations, thus minimizing the effects of human error.
- Allows focused cleaning of large area surveys by multiple users while maintaining control by the lead data processor.
- Sub projects only require a Qimera Clean license and therefore will reduce the total cost of ownership of the software for a data processing team.
- Data cleaning can be performed by less experienced personnel, again reducing project costs.
- Sub projects contain QPD files only and are thus limited to cleaning only. This reduces the risk of less experienced personnel accidentally applying correctors or making configuration changes.
- Sub projects can be moved off the network to a local machine to overcome slow network bandwidth, while maintaining the integrity of the data by keeping the master copy.
The image below shows the main project being cut into a series of nine sub-projects with the new "Create Cleaning Projects" dialog.
The user specifies the cleaning project base name, location for output and the number of rows and tiles to cut the project into.
Alternately, the lead project surveyor can also designate a particular area for a cleaning project using the rectangular selection tool. The dialog to create a cleaning project will use this area instead.
The image below shows the data from the point of view of the person cleaning one of the sub projects.
They see the QPDs from the main project that overlap their work area and they see the outline of the entire project as well as the outline of their sub area.
Since it is only QPDs that are brought into a cleaning project, the only actions that are permissible are data cleaning.
Compartmentalizing the data into cleaning projects limits the risk of accidental re-processing by inexperienced or curious data processors who like to explore what all the buttons do.
Once the data cleaner's work is done, the main project is opened up by the lead surveyor and they can import the cleaning from the cleaning project.
Only the editing that was done inside the cleaning area limit rectangle is brought back into the main project, further protecting the main project from overzealous cleaning that may have been done beyond the data cleaner's work area.
