QPA Reference Manual
QPS Plugin Architecture (QPA)
Reference Manual
Extending the capabilities of the Fledermaus Suite of Tools
Version 1.0 (Qt 4.7.X)
Introduction
Readers of this document are expected to be familiar with software development on Windows, Mac and Linux platforms and to understand the fundamentals of C++ as well as the development tools used on each platform (i.e. Visual Studio, XCode, etc.). This document will cover the general interface specification as well as some examples on how to write a plugin. Samples will be done on the Windows platform with platform specific examples done in following appendices.
This document is a reference guide to the classes involved in the QPS Plugin Architecture. For information on building plugins, please see the Developer Guide.
Interface Architecture
The plugin interface architecture shown in Figure 1 provides the mechanism of communication between the plugin and its host. This example shows the interface for the FMMidwater tool, but each application supported by QPA has its own specific application and plugin interface derived class.
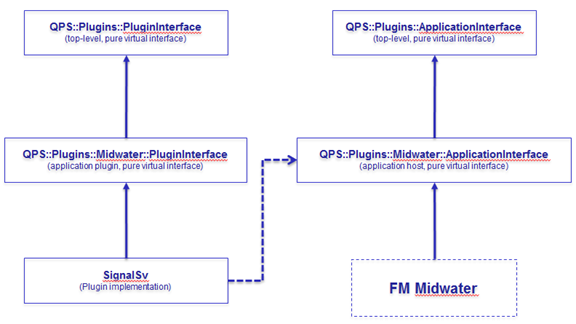
Figure 1 - Interface Architecture
If you are creating a plugin for a specific application such as FMMidwater, you must derive your plugin class from the Midwater specific PluginInterface class. All class types within the QPA use namespaces to reduce potential naming collisions. For the QPA, the primary namespace is QPS::Plugins. There are other namespaces exposed by the interface specification but these will be discussed later.
Plugin Interfaces
QPS::Plugins::PluginInterface
This is the base class for all plugins. Each derived plugin must implement all of the methods within the interface. It is defined in the file QPS_PluginInterface.h that resides in the QPS_PluginSDK/libsrc/plugin_api/external directory.
Initialize
Arguments: QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface * pApp
Returns: None
This method is called by the host application when the plugin is first loaded. The host passes a pointer to a QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface object that the plugin can store locally. This pointer is used to access the virtual interface that talks back to the application as shown in Error! Reference source not found. and defined later in this chapter.
CanRun
Arguments: QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface * pApp
Returns: bool
This method is called by the host application when the plugin GUI connection is about to be activated. This allows the plugin to determine if it is ready to run. For example, if the plugin requires a survey line to be selected, it could ask the application for the current line selection. The plugin could then return true or false based on this query. The application will then enable or disable the GUI element connected to the plugin in the appropriate manner.
DLLName
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method is will return the plugin DLL name. This is the target DLL name without the extension. For example, the Datagram Viewer plugin discussed later in this document returns “sh_datagramViewer”.
Name
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the plugin display name. This string is used the the GUI element of the application. For example, the Datagram Viewer plugin discussed later in this document returns “Datagram Viewer”.
Organization
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the plugin responsible organization. Depending on the plugin type, this string will be used to create a sub-menu to group plugins by Organization. For example, if CCOM develops shared tool plugins, they will appear under the Tools menu of the application under a sub-menu titled “CCOM”
Type
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the host application to retrieve the plugin type. The type is used by the host application to determine where in the GUI the plugin will appear. If the plugin is derived directly from this base class, there is only one possible type, eSharedTool.
IsModal
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method is tells the application host if the plugin runs as a model dialog or if it can run modeless. If it can run modeless, some of the derived interfaces allow connections of plugin Qt slots to application host Qt signals.
QtObject
Arguments: None
Returns: QObject*
This returns a “this” pointer to the plugin object.
Help
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This returns a formatted string summarizing the capabilities of the plugin. This string is shown when executing a plugin by the use of a modifier key or in the application about box plugin section.
Execute
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application host when the user wants to run the plugin. For simple plugins based on this interface, no parameters are passed and the plugin can return success by passing back 0.
ShowPreferences
Arguments: None
Returns: None
This is called by the application to allow the plugin to show a preferences dialog. Preferences can be stored globally by the plugin or in the users current FM project.
GetStatus
Arguments: None
Returns: StatusTypeEnum
This allows the plugin to tell the application its development state. Possible options are eExperimental, eDemo, eBeta and eReleased.
QPS::Plugins::PluginInterface (top-level, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::Midwater::PluginInterface (application plugin, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::Midwater::PluginInterface
This derived interface provides the methods specific to FMMidwater plugins. Each plugin must implement all methods within this interface.
ConvertSignal
Arguments: Pio_BaseTypes::SourceFileFormatEnum sfe
FomatGWC::InterfaceWaterColumn* wcIn
FormatGWC::InterfaceWaterColumn* wcOut
Returns: SVint
When a plugin is of type eSignalConvert, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This method is called when the plugin is active any time data is to be converted for display or export. Success should return 0.
SignalName
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method should return the name of the signal conversion (i.e. Power, TS, sV).
SignalUnit
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method should return the units of the signal conversion (i.e. dB).
QPS::Plugins::PluginInterface (top-level, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::Midwater::PluginInterface (application plugin, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::GeocoderToolbox::PluginInterface
This derived interface provides the methods specific to FMGT plugins. Each plugin must implement all methods within this interface.
Execute_PreProcess
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type ePreProcess, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 - FMGT Process Configuration
Execute_ProcessBathy
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type eProcessBathy, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
Execute_ProcessImagery
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type eProcessImagery, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
Execute_ProcessCorrections
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type eProcessCorrections, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
Execute_ProcessAssemble
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type eProcessAssemble, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
Execute_ProcessAVG
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type eProcessAVG, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
Execute_ProcessAntialias
Arguments: PluginProcessingParameters* data
Returns: bool
When a plugin is of type eProcessAntialias, the host application will call this method instead of the “Execute” call. This plugin is part of the processing pipeline of FMGT and is configured for using the configuration dialog shown in Figure 2.
QPS::Plugins::PluginInterface (top-level, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::SF::PluginInterface (application plugin, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::SF::PluginInterface
This derived interface provides the methods specific to SF (Scientific Parser) plugins. Each SF plugin must implement all methods within this interface. An SF plugin is designed to stream soundings (plus flags) from a specific file format. For example, SF support of GSF returns 1 sounding at a time with it’s associated edit flags and navigation information.
CanDecode
Arguments: QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface* pApp
const char* filename
Returns: bool
This is called by the application to determine if a specific file can be decoded by the scientific parser plugin. Return values are true or false.
Create
Arguments: QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface* pApp
Returns: Sf_IBaseReader*
This is called by the application to have the plugin create an instance of the Sf_IBaseReader class. The object will then be used for decoding. The application handles destruction of the object.
QPS::Plugins::SF::SF_IBaseReader
This interface is the primary method of communication between Fledermaus and DMagic gridding operations and the underlying file format.
Cleanup
Arguments: None
Returns: None
This is called by the application to have the plugin cleanup any allocate data.
StartReading
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin prepare to begin reading soundings from the supported file format. Typically the plugin will open a FILE* for reading. The method would return SF_OK on success or one of the defined SF_ERROR_XXX strings defined by Sf_Errors.h.
EndReading
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin end reading operations. At this point the plugin would close the FILE handle opened by the StartReading method.
GetNextFullRecord
Arguments: SVint* errorCode
Returns: Sf_FullRecord*
This is called by the application to have the plugin retrieve the next record (sounding data). If at the end of the file, the plugin should return a NULL pointer;
StartWriting
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin prepare to begin writing data to the associated file. Typically the plugin will open a FILE* for writing. The method would return SF_OK on success or one of the defined SF_ERROR_XXX strings defined by Sf_Errors.h.
EndWriting
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin end write operations. At this point the plugin would close the FILE handle opened by the StartWriting method.
WriteNextFullRecord
Arguments: Sf_FullRecord*
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin write a full record of data to the sounding file. Success should return SF_OK.
3.5.8 WriteNextRecord
Arguments: Sf_OutputRecordStruct*
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin write a full partial record of data including only the x, y, z and validity flag. Success should return SF_OK.
3.5.9 StartUnloading
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin prepare to begin unloading data to the associated file. Typically the plugin will open a FILE* for writing. The method would return SF_OK on success or one of the defined SF_ERROR_XXX strings defined by Sf_Errors.h.
3.5.10 EndUnloading
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin end unload operations. At this point the plugin would close the FILE handle opened by the StartWriting method.
3.5.11 UnloadRecord
Arguments: SVint recordNum
SVint subRecordNum
SVushort flags
SVdouble depth
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to have the plugin unload edit information to the associated file. The record (ping), subrecord (beam) and flags are passed in as well as the depth. Return SF_OK for successful operation.
3.5.12 GuessNumFields
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
Typically only used by ASCII parsers to return the number of fields present.
3.5.13 GetHeader
Arguments: None
Returns: Sf_Header
Returns the Sf_Header structure.
3.5.14 GetPercentRead
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
Returns 0.0 to 100.0. Indicates progress of the parser for display to the user in the main GUI.
3.5.15 SetInput
Arguments: const char *
Returns: None
This is called by the application to set the input filename for the parser. The parser should save the file locally. This is the file used for read operations.
3.5.16 SetOutput
Arguments: const char *
Returns: None
This is called by the application to set the output filename for the parser. The parser should save the file locally. This is the file used for write/unload operations.
3.5.17 GetFieldSetup
Arguments: None
Returns: Sf_FieldSetup*
This is called by the application to retrieve the field setup for display in a dialog.
3.5.18 GetReaderAbility
Arguments: None
Returns: Sf_ReaderAbility*
This is called by the application to retrieve the reader capabilities to know if this parser can, for instance, unload data back to the file.
3.5.19 GetNumRecords
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to retrieve the total number of records present in the file (this may not be known for ASCII files).
3.5.20 SetOutputMetaData
Arguments: Sf_MetaData*
Returns: None
This is called by the application to set the output metadata structure.
3.5.21 SetOutputFields
Arguments: SVint xField
SVint yField
SVint zField
Returns: None
This is called by the application to set the x, y, z fields of a generic ASCII parser. This routine is typically unsed in other SF plugins.
3.5.22 SetOutputFieldSetup
Arguments: Sf_FieldSetup*
Returns: None
This is called by the application to set the field setup of the plugin.
3.5.23 GetRecordSize
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to get the size of each record.
3.5.24 SetCurrentLineNum
Arguments: SVint
Returns: None
This is called by the application to set the current line number being processed.
3.5.25 GetFormatSpecificCode
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This is called by the application to get the current record.
3.5.26 SetReadNav
Arguments: SVint
Returns: None
This is called by the application to tell the parser to read navigation information.
3.5.27 SetFieldInfo
Arguments: SVint index
Const char* fieldname
SVvariantType type
SVint baseField
Returns: None
The plugin uses this to setup specific fields for processing. See the sf_readerDEMO constructor for an example of usage.
3.5.28 SetFlagInfo
Arguments: SVint index
Const char* flagname
SVint fieldMapping
Returns: None
The plugin uses this to setup specific flags for processing. See the sf_readerDEMO constructor for an example of usage.
3.5.29 SetHeaderField
Arguments: SVint index
Const char* headername
SVvariantType type
SVint baseField
Returns: None
The plugin uses this to setup header fields for processing. See the sf_readerDEMO plugin for an example of usage.
3.5.30 InitNumFields
Arguments: SVint
Returns: None
The plugin uses this initialize the total number of fields to be mapped. . See the sf_readerDEMO constructor for an example of usage.
3.5.31 InitNumFlags
Arguments: SVint
Returns: None
The plugin uses this initialize the total number of flags to be mapped. . See the sf_readerDEMO constructor for an example of usage.
3.5.32 InitNumHeaderFields
Arguments: SVint
Returns: None
The plugin uses this initialize the total number of header fields to be mapped. . See the sf_readerDEMO constructor for an example of usage.
Chapter 4 - Application Interfaces
4.1 QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface
This base class for all application hosts. All applications supporting plugin hosting implement this interface which allows “Shared Tool” plugins to be used across multiple applications. This interface is much more extensive as it gives the plugin access to the powerful capabilities of the host application. Further host specific derivations further extend these capabilities (i.e. QPS::Plugins::Midwater::ApplicationInterface).
4.1.1 VaDebug
Arguments: const char *fmt, …
Returns: None
This method allows the plugin to send a formatted message to the console window. If the application is run from the console or run with the “-debug” argument, a console window will appear beside the application. All VaDebug messages are sent to the console. Sample usage is descsribed below.
SVfloat myval = -89.2
m_applicationInterface->VaDebug(“Computation of %s is %5.1f”, “Depth”, myval);
Console output would be:
Computation of Depth is -89.2
4.1.2 ErrorMsg
Arguments: const char *fmt, …
Returns: None
This method will display an error dialog in the hosting application. The following code will display the dialog box in Figure 3.
SVfloat myval = -89.2
m_applicationInterface->ErrorMsg(Computation of “%s is %5.1f”, “Depth”, myval);
4.1.3 WarningMsg
Arguments: const char *fmt, …
Returns: None
This method will display an error dialog in the hosting application. The following code will display the dialog box in Figure 4.
SVfloat myval = -89.2
m_applicationInterface->WarningMsg(Computation of “%s is %5.1f”, “Depth”, myval);
4.1.4 InfoMsg
Arguments: const char *fmt, …
Returns: None
This method will display an error dialog in the hosting application. The following code will display the dialog box in Figure 5.
SVfloat myval = -89.2
m_applicationInterface->InfoMsg(Computation of “%s is %5.1f”, “Depth”, myval);
Figure 3 - Error Dialog
Figure 4 - Warning Dialog
Figure 5 - Info Dialog
4.1.5 FileLength
Arguments: QString
Returns: SVint64
This method will return the length of the passed in filename in bytes.
4.1.6 FilePosition
Arguments: FILE*
Returns: SVint64
This method will return the current file position of the opened file.
4.1.7 CreateIndex
Arguments: QString
Returns: Pio_IBaseIndex*
This method will create a packetized file index (PIO) from the passed in filename. This index can then be used do decode packets of a given file format. PIO is described in detail in Chapter 4. This object must be destroyed using the overloaded DeleteObject() method.
4.1.8 CreateDecoder (overloaded)
Arguments: Pio_IBaseIndex*
Returns: Pio_IBaseDecoder*
This method will create a PIO file decoder on a given index. A decoder is used to read packets from a file based on a specific index. PIO is described in detail in Chapter 4. This object must be destroyed using the overloaded DeleteObject() method.
4.1.9 CreateDecoder (overloaded)
Arguments: Pio_BaseTypes::SourceFileFormatEnum
Returns: Pio_IBaseDecoder*
This method will create a PIO file decoder based on the passed in format type. This object must be destroyed using the overloaded DeleteObject() method.
4.1.10 IndexType
Arguments: QString
Returns: Pio_BaseTypes::SourceFileFormatEnum
This method will return the index type of a passed in file name. See Pio_BaseTypes.h for all possible return types.
4.1.11 CreateNavManager
Arguments: None
Returns: Pio_INavMgr*
This method will create an empty Pio_INavMgr object. This object must be destroyed using the overloaded DeleteObject() method.
4.1.12 LoadNavigation
Arguments: Pio_INavMgr*
Pio_BaseTypes::NavigationRecord*
SVdouble t
Returns: Pio_INavMgr*
This method will use the timestamp “t” to retrieve a time interpolated lookup for all available navigation information in the passed in Pio_INavMgr. It will load this data into the passed in NavigationRecord object.
4.1.13 DeleteObject (overloaded)
Arguments: Pio_IBaseIndex*
Returns: None
This method will delete the passed in object.
4.1.14 DeleteObject (overloaded)
Arguments: Pio_IBaseDecoder*
Returns: None
This method will delete the passed in object.
4.1.15 DeleteObject (overloaded)
Arguments: Pio_INavMgr*
Returns: None
This method will delete the passed in object.
4.1.16 PickUtmFromPosition
Arguments: SVdouble x
SVdouble y
Char* wktBuf
SVint wktSize
Returns: bool
This method will retrieve the UTM WKT string for a given position. The user must pass in a pointer to a character buffer and size for which the string will be copied. The return type indicates success of the operation (true/false).
4.1.17 ShowHideWaitCursor
Arguments: bool
Returns: None
This method will show or hide the wait cursor on the main application based on the value (true/false) of the passed in argument.
4.1.18 Application
Arguments: None
Returns: QWidget*
This method will return the main Qt Widget pointer of the host application.
4.1.19 ApplicationName
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the name of the host application.
4.1.20 ApplicationCompany
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the name of the host application organization (“QPS”).
4.1.21 SaveFileDialog
Arguments: QString fileFilter
QString caption
QString startingFolder
Returns: QString
This method will display a save file dialog for use in retrieving a save file name from the host system. A sample usage of this method is shown below with the accompanying dialog.
// Retrieve the last data folder from the application interface
QString startFolder = m_app->GetLastDataFolder();
// Call the SaveFileDialog
QString s = m_app->SaveFileDialog("Bitmap Files (*.bmp);;JPEG Files(*.jpg);;PNG Files(*.png);; ",
"Save As", startFolder );
Figure 6 – File Save Dialog
4.1.22 OpenFilesDialog
Arguments: QString fileFilter
QString caption
QString startingFolder
Returns: QStringList
This method will display an open file dialog that allows multiple selections. It will return a QStringList containing the selected files. A sample usage of this method is shown below with the accompanying dialog.
// Retrieve the last data folder from the application interface
QString startFolder = m_app->GetLastDataFolder();
// Call the SaveFileDialog
QString s = m_app->OpenFilesDialog("Bitmap Files (*.bmp);;JPEG Files(*.jpg);;PNG Files(*.png);; ",
"Select Files", startFolder );
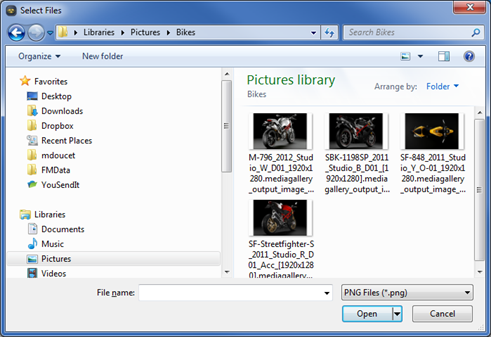
Figure 7 - Open Files Dialog
4.1.23 OpenFileDialog
Arguments: QString fileFilter
QString caption
QString startingFolder
Returns: QString
This method will display an open file dialog that allows single selection. It will return a QString containing the selected file. A sample usage of this method is shown below with the accompanying dialog.
// Retrieve the last data folder from the application interface
QString startFolder = m_app->GetLastDataFolder();
// Call the SaveFileDialog
QString s = m_app->OpenFileDialog("Bitmap Files (*.bmp);;JPEG Files(*.jpg);;PNG Files(*.png);; ",
"Select File", startFolder );Figure 8 - Open File Dialog
4.1.24 OpenFolderDialog
Arguments: QString caption
QString startingFolder
Returns: QString
This method will display an open folder dialog. It will return a QString containing the selected folder. A sample usage of this method is shown below with the accompanying dialog.
// Retrieve the last data folder from the application interface
QString startFolder = m_app->GetLastDataFolder();
// Call the SaveFileDialog
QString s = m_app->OpenFolderDialog("Select Folder", startFolder );
Figure 9 - Open Folder Dialog
4.1.25 MetadataFolder
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the path of the Fledermaus suite Metadata folder. This folder contains all of the index files created by PIO.
4.1.26 GetLastDataFolder
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the path set by SetLastDataFolder.
4.1.27 SetLastDataFolder
Arguments: QString
Returns: None
This method will set the location of the last data folder.
4.1.28 GetProjectFolderPath
Arguments: QString
Returns: QString
This method will return the desired folder that is part of the project path. For example, FMGT and FMMidwater share project folder layouts. They both have a top level “myproject/Source” folder. By passing “Source” as the argument, you will retrieve the full path name of the project’s Source folder.
4.1.29 GetProjectOutputPath
Arguments: QString
Returns: QString
This method will return the desired folder that is part of the project\output path. For example, FMGT has a myproject/Output/SD folder. By passing “SD” as the argument, you will retrieve the full path name of the project’s Output/SD folder.
4.1.30 GetPluginSettingsPath
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will return the default location of the user path for plugin settings. By default this is ~username/FMData/PluginSettings.
4.1.31 GetWktString
Arguments: QString
Returns: QString
This method will return WKT string of a specific coordinate name. A sample of a Fledermaus coordinate name is “FP_WGS_84_UTM_zone_1N”.
4.1.32 TransformByName (overloaded)
Arguments: QString coordNameIn
QString coordNameOut
SVdouble &x,
SVdouble &y
Returns: bool
This method will return the input x/y references from the input coordinate name string to the output coordinate name string. If successful, it will return true.
4.1.33 TransformByName (overloaded)
Arguments: QString coordNameIn
QString coordNameOut
SVdouble *x
SVdouble *y
SVdouble *z
SVint count
Returns: bool
This method will transform the x,y,z arrays from the input coordinate name string to the output coordinate name string. If successful, it will return true.
4.1.34 TransformByWKT (overloaded)
Arguments: QString wktIn
QString wktOut
SVdouble &x,
SVdouble &y
Returns: bool
This method will return the input x/y references from the input WKT string to the output WKT string. If successful, it will return true.
4.1.35 TransformByWKT (overloaded)
Arguments: QString wktIn
QString wktOut
SVdouble *x
SVdouble *y
SVdouble *z
SVint count
Returns: bool
This method will transform the x,y,z arrays from the input WKT string to the output WKT string. If successful, it will return true.
4.1.36 PickCoordWkt
Arguments: QString
Returns: QString
This method will display the Fledermaus coordinate picking widget. The initial coordinate system will be the passed in WKT string. It will return the selected WKT string or an empty string if cancelled. An example with the associated dialog is shown in Figure 10.
QString wkt = m_applicationInterface->PickCoordWkt(
m_applicationInterface->GetWktString("FG_WGS_84"));
Figure 10 - Coordinate Selection Dialog
4.2
QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface (top-level, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::Midwater::ApplicationInterface (application host, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::Midwater::ApplicationInterface
This derived interface provides the methods specific to FMMidwater host applications. It provides access to exended capabilities available only via the FMMidwater application.
4.2.1 AddSourceFilesToProject
Arguments: QStringList
Returns: None
This method is called by the plugin to add Source files to the FMMidwater project.
4.2.2 AddNavFilesToProject
Arguments: QStringList
Returns: None
This method is called by the plugin to add Navigation files to the FMMidwater project.
4.2.3 AddGwcFilesToProject
Arguments: QStringList
Returns: None
This method is called by the plugin to add GWC files to the FMMidwater project.
4.2.4 GetSelectedLineName
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method returns the currently selected line in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.5 GetCurrentGwcPing
Arguments: None
Returns: FormatGWC::InterfaceWaterColumn*
This method returns a pointer to the current water column data being displayed in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.6 GetCurrentGwcSourceType
Arguments: None
Returns: Pio_BaseTypes::SourceFileFormatType
This method returns the source type of the data that created the currently selected GWC.
4.2.7 GetSignalType
Arguments: None
Returns: FormatGWC::SignalTypeEnum
This method returns the selected single type as indicated in the FMMidater GUI.
4.2.8 GetSignalTypeString
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method returns the string name of the selected signal type.
4.2.9 ConvertToSignalTypeString
Arguments: FormatGWC::InterfaceWaterColumn *src
FormatGWC::InterfaceWaterColumn *dest
Pio_BaseTypes::SourceFileFormatType sfe,
FormatGWC::SignalTypeEnum st,
QString stName
Returns: bool
This method will allow the plugin to call FMMidwater to convert data from one signal type to another. For example, if the plugin reads amplitude data, it could have FMMidwater convert it to target strength. If a custom signal type is used, the plugin must pass the signal type name (stName) so that FMMidwater can select the correct plugin.
4.2.10 LogMessage
Arguments: SVint msgType
QString const char* msg, …
Returns: void
This method is used by the plugin to display a formatted message in the FMMidwater message window. Message types are error (-1), warning (2) or information (1).
4.2.11 GetCurrentGWC
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method returns the currently selected GWC filename.
4.2.12 GetSelectedArea (overloaded)
Arguments: SVdouble &xMin
SVdouble &xMax
SVdouble &yMin
SVdouble &yMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected area in the map window of FMMidwater.
4.2.13 GetSelectedArea (overloaded)
Arguments: Sv_Extents2D &ext
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected area in the map window of FMMidwater.
4.2.14 GetHistogramBounds
Arguments: SVdouble &valMin
SVdouble &valMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected histogram bounds from the histogram control in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.15 GetHistogramClip
Arguments: SVboolean &clipMin
SVboolean &clipMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected clipping states from the histogram control in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.16 GetPingBounds
Arguments: SVdouble &valMin
SVdouble &valMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected ping bounds as selected in the beam or stacked views of the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.17 GetRangeBounds
Arguments: SVdouble &valMin
SVdouble &valMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected range bounds as selected by the range control widget in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.18 GetBeamBounds
Arguments: SVdouble &valMin
SVdouble &valMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected beam bounds as selected by the beam control widget in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.19 GetDepthBounds
Arguments: SVdouble &valMin
SVdouble &valMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected depth bounds as selected by the depth control widget in the FMMidwater GUI.
4.2.20 GetCurrentTime
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method returns the current time of the time control in the FMMidwater GUI. The time is a Jan-1-1970 reference time in seconds.
4.2.21 IsFanView
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method returns true if the primary FMMidwater display is in “Fan” mode.
4.2.22 IsBeamView
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method returns true if the primary FMMidwater display is in “Beam” mode.
4.2.23 IsStackedView
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method returns true if the primary FMMidwater display is in “Stacked” mode.
4.2.24 UpdateView
Arguments: None
Returns: None
This method triggers a redraw of the FMMidwater water column display widgets.
4.3
QPS::Plugins::ApplicationInterface (top-level, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::GeocoderToolox::ApplicationInterface (application host, pure virtual interface) |
QPS::Plugins::GeocoderToolbox::PluginInterface
This derived interface provides the methods specific to FMGT host applications. It provides access to exended capabilities available only via the FMGT application.
4.3.1 CreateLine
Arguments: None
Returns: QPS::GeocoderToolbox::LineInterface*
This method will create a GT line object. The plugin must use the DeleteLine method to destroy this object.
4.3.2 GetCurrentLine
Arguments: None
Returns: QPS::GeocoderToolbox::LineInterface*
This method will return the currently selected line in the FMGT GUI.
4.3.3 GetLine
Arguments: SVint
Returns: QPS::GeocoderToolbox::LineInterface*
This method will return a line object by index from the FMGT project.
4.3.4 GetLineCount
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method will return the total number of lines loaded in FMGT.
4.3.5 FlushLine
Arguments: QPS::GeocoderToolbox::LineInterface*
Returns: None
This method will flush all memory allocated in a line for re-use by the plugin.
4.3.6 DeleteLine
Arguments: QPS::GeocoderToolbox::LineInterface*
Returns: None
This method will delete a line object allocated by a previous CreateLine call.
4.3.7 IsLineChecked
Arguments: SVint
Returns: bool
This method will return true/false based on the check-state of the line number passed in.
4.3.8 GetSelectedArea (overloaded)
Arguments: SVdouble &xMin
SVdouble &xMax
SVdouble &yMin
SVdouble &yMax
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected area in the map window of FMGT.
4.3.9 GetSelectedArea (overloaded)
Arguments: Sv_Extents2D &ext
Returns: bool
This method returns the currently selected area in the map window of FMGT.
4.3.10 GetSensorConfig
Arguments: None
Returns: FormatGWC::InterfaceInstallationParameters* config
This method will return the generic sensor configuration object as defined by the FMGT project (i.e. transducer linear/angular offsets, etc.)
4.3.11 AddSourceFilesToProject
Arguments: QStringList
Returns: None
This method is called by the plugin to add Source files to the FMGT project.
4.3.12 LogMessage
Arguments: SVint msgType
QString const char* msg, …
Returns: void
This method is used by the plugin to display a formatted message in the FMGT message window. Message types are error (-1), warning (2) or information (1).
4.3.13 ProjectCoordsToLatLon
Arguments: SVint count
SVdouble* x
SVdouble* y
Returns: None
This method is called by the plugin to transform project coordinates to latitude longitude. FMGT will use the current project coordinate system (input/output) to transform the data.
4.3.14 LatLonToProjectCoords
Arguments: SVint count
SVdouble* x
SVdouble* y
Returns: None
This method is called by the plugin to transform latitude/longitude coordinates to project coordinates. FMGT will use the current project coordinate system (input/output) to transform the data.
4.3.15 Mosaic_IsSelected
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method is called by the plugin to determine if a Mosaic Layer is currently selected in the FMGT tree view widget.
4.3.16 Mosaic_GetNumColumns
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the number of columns for the currently selected Mosaic Layer.
4.3.17 Mosaic_GetNumRows
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the number of rows for the currently selected Mosaic Layer.
4.3.18 Mosaic_GetWidth
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the width (in project units) for the currently selected Mosaic Layer.
4.3.19 Mosaic_GetHeight
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the height (in project units) for the currently selected Mosaic Layer.
4.3.20 Mosaic_GetValue
Arguments: SVint column
SVint row
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the value of the currently selected Mosaic Layer at a particular row/column location.
4.3.21 Mosaic_GetValue
Arguments: SVdouble xPos
SVdouble yPos
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the value of the currently selected Mosaic Layer at a particular geographic (projected) location.
4.3.22 Mosaic_GetDataRange
Arguments: SVdouble &minValue
SVdouble &maxValue
Bool bActive
Returns: bool
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the data range of the currently selected Mosaic Layer. The bActive flag indicates whether the active range as selected by the histogram widget or the full range will be returned.
4.3.23 Mosaic_GetExtents
Arguments: Sv_Extents2D &ext
Returns: bool
This method returns the geographic extents (projected) of the currently selected Mosaic Layer.
4.3.24 Stat_IsSelected
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method is called by the plugin to determine if a Statistic Layer is currently selected in the FMGT tree view widget.
4.3.25 Stat_GetNumColumns
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the number of columns for the currently selected Statistic Layer.
4.3.26 Stat_GetNumRows
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the number of rows for the currently selected Statistic Layer.
4.3.27 Stat_GetWidth
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the width (in project units) for the currently selected Statistic Layer.
4.3.28 Stat_GetHeight
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the height (in project units) for the currently selected Statistic Layer.
4.3.29 Stat_GetValue
Arguments: SVint column
SVint row
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the value of the currently selected Statistic Layer at a particular row/column location.
4.3.30 Stat_GetValue
Arguments: SVdouble xPos
SVdouble yPos
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the value of the currently selected Statistic Layer at a particular geographic (projected) location.
4.3.31 Stat_GetDataRange
Arguments: SVdouble &minValue
SVdouble &maxValue
Bool bActive
Returns: bool
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the data range of the currently selected Statistic Layer. The bActive flag indicates whether the active range as selected by the histogram widget or the full range will be returned.
4.3.32 Stat_GetExtents
Arguments: Sv_Extents2D &ext
Returns: bool
This method returns the geographic extents (projected) of the currently selected Statistic Layer.
4.3.33 Ara_IsSelected
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method is called by the plugin to determine if a ARA Layer is currently selected in the FMGT tree view widget.
4.3.34 Ara_GetNumColumns
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the number of columns for the currently selected ARA Layer.
4.3.35 Ara_GetNumRows
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the number of rows for the currently selected ARA Layer.
4.3.36 Ara_GetWidth
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the width (in project units) for the currently selected ARA Layer.
4.3.37 Ara_GetHeight
Arguments: None
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the height (in project units) for the currently selected ARA Layer.
4.3.38 Ara_GetValue
Arguments: SVint column
SVint row
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the value of the currently selected ARA Layer at a particular row/column location.
4.3.39 Ara_GetValue
Arguments: SVdouble xPos
SVdouble yPos
Returns: SVdouble
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the value of the currently selected ARA Layer at a particular geographic (projected) location.
4.3.40 Ara_GetDataRange
Arguments: SVdouble &minValue
SVdouble &maxValue
Bool bActive
Returns: bool
This method is called by the plugin to retrieve the data range of the currently selected ARA Layer. The bActive flag indicates whether the active range as selected by the histogram widget or the full range will be returned.
4.3.41 Ara_GetExtents
Arguments: Sv_Extents2D &ext
Returns: bool
This method returns the geographic extents (projected) of the currently selected ARA Layer.
Chapter 5 - PIO Interfaces
PIO provides plugin developers with decoding capability for all sonar formats supported by FMMidwater and FMGT. It consists of a set of supported type definitions, a file indexer and a file decoder. The index is the base component that is used to access packet data in a non-linear fashion directly from the sonar format.
The indexer creates a disk based metadata file that is re-used each time the sonar file is open. PIO also knows if the file has been altered requiring a rebuild of the index. The user can also dynamically create sub-indices of a particual packet type to allow fast decoding of specific sonar data.
Once an index has been created for a file, the user creates a decoder that is specific to the file type. This decoder is then used in tandem with the index to decode packet data from sonar file.
Figure 11 - PIO Indexing |
Metadata |
5.1 PIO_IBaseIndex
This class interface provides access to indexing utilities. Formats currently supported by PIO include:
.ALL Kongsberg
.RAW Simrad
.S7K Reson
.GWC Generic Watercolumn Format
.SEG SEGY
.XTF Triton
.EK5 Simrad
.83X Imagenex
.sbet POSPac
.000 POSMV
.GSF SAIC
.SDF Klein
.SDF2 Klein
.DBM DeBeers Mining
5.1.1 GetIndexRecord
Arguments: None
Returns: Pio_BaseTypes::IndexRecord*
This method returns a pointer to the array of index records for this index.
5.1.2 GetIndexHeader
Arguments: None
Returns: Pio_BaseTypes::IndexHeader*
This method returns a pointer to the file header for this index.
5.1.3 CreateNavManager
Arguments: SVint positionSource
SVint motionSource
SVint headingSource
Returns: Pio_INavMgr*
This method returns a pointer to a new Pio_INavMgr object containing all relevant navigation information for the associated file. For Kongsberg data, you must ensure that you include the correct “source” information. For example:
FormatGWC::InterfaceInstallationParameters installParams;
QPS::PIO::Pio_INavMgr* mgr = NULL;
myIndex->GetInstallationParameters(&installParams);
mgr = myIndex->CreateNavManager(installParams->APS+1, 1, installParams->AHS);
You must remember to use the DeleteObject() method from the ApplicationInterface pointer in your plugin to delete this object.
5.1.4 CreateDecoder
Arguments: None
Returns: Pio_IBaseDecoder*
This method returns a pointer to a new Pio_IBaseDecoder object. It can then be used to begin decoding data from a sonar file. See the section on Pio_IBaseDecoder for example usage.
You must remember to use the DeleteObject() method from the ApplicationInterface pointer in your plugin to delete this object.
5.1.5 CreateSubIndex
Arguments: SVint datagramType
SVint systemId *future upgrade
SVint wrappedDatagram *future ugrade
Returns: Pio_IBaseIndex*
This method returns a pointer to a new Pio_IBaseIndex containing only the requested packet type.
You must remember to use the DeleteObject() method from the ApplicationInterface pointer in your plugin to delete this object.
5.1.6 CountDatagrams
Arguments: SVint datagramType
Returns: SVint
This method returns the packet count of the specific datagram type within the file referenced by the index.
5.1.7 ContainsDatagram
Arguments: SVint datagramType
Returns: SVboolean
This method returns truen if the index contains the specific packet type, false otherwise.
5.1.8 SetTimeReference
Arguments: SVdouble t
Returns: None
This method is important when working with POSPac data. The timestamps in POSPac data are in seconds and begin at midnight of the week recording started. If you building a Pio_INavMgr object from this data, you will need to have the navigation timestamps in the proper 1/1/1970 reference frame to match to ping time stamps. Call this method with the IndexHeader.startTime1970 of the file you want to do navigation matching on.
5.1.9 GetInstallationParameters
Arguments: FormatGWC::InterfaceInstallationParameters*
Bool bApplied
Returns: bool
This method loads the generic installation parameter information from any of the supported file types.
5.2 PIO_IBaseDecoder
This class interface provides access to file decoding utilities. This object paired with a Pio_IBaseIndex object allows a developer to decode any of the supported file types.
5.2.1 Open
Arguments: const char* filename
Returns: bool
This method opens a file for high speed decoding.
5.2.2 Close
Arguments: None
Returns: bool
This method closes a file previously opened for decoding.
5.2.3 CreatePacket
Arguments: SVint packetType
Returns: PacketCommon* pkt
This method creates a packet interface that can be used during decoding operations. For example:
FormatALL::InterfaceXYZ* pkt =
(FormatALL::InterfaceXYZ*)mydecoder->CreatePacket(FormatALL::eXYZ);
Packet object must be deleted using the DeletePacket() method listed next.
5.2.4 DeletePacket
Arguments: PacketComon* pkt
Returns: None
This method deletes a packet interface object previous created using CreatePacket(). For example:
// Create the XYZ packet
FormatALL::InterfaceXYZ* pkt =
(FormatALL::InterfaceXYZ*)mydecoder->CreatePacket(FormatALL::eXYZ);
// Delete the XYZ packet
mydecoder->DeletePacket(pkt);
5.2.5 FRead
Arguments: Pio_IBaseIndex* index
SVint recid
void* data
Returns: bool
This method decodes a data packet from a sonar file. For example, to decode the 10th (of 100) XYZ packets from my sonar file:
// Create the XYZ packet
FormatALL::InterfaceXYZ* pkt =
(FormatALL::InterfaceXYZ*)mydecoder->CreatePacket(FormatALL::eXYZ);
// Open the file for reading
if (mydecoder->Open(“myfile.all”))
{
// Read the 10th packet
if (mydecoder->FRead(myindex, 10, xyz))
{
// Successful read! Do something…
}
// Close the file
Mydecoder->Close();
}
// Delete the packet
mydecoder->DeletePacket(pkt);
5.2.6 FReadHeader
Arguments: Pio_IBaseIndex* index
SVint recid
void* data
Returns: bool
This method behaves like theFRead call except that it only reads the “header” section of a packet. For example, packets such as multibeam and snippet data contain a separate header section. This method will read the header and skip the beam data.
5.2.7 MRead
Arguments: Sv_IMemoryBlock* mp
SVint pktType
void* data
SVuint flags
Returns: bool
This method is used to decoder packets directly from a memory block. This is useful if you are decoding data from formats that “wrap” other manufacturer packet data, like XTF.
Possible flags are:
FormatXTF::MREAD_FLAG_SKIP_PINGHEADER Skips reading of ping header during decode operation
FormatALL::MREAD_FLAG_SKIP_NUMBYTES Skips reading of numberOfBytes field during decode operaion
5.2.8 MRead
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint64
This method returns the size of the file attached to the decoder.
5.2.9 Create
Arguments: const char* filename
Returns: bool
This method creates a new file for “encoding”. Encoding involves FWrite operations and is only supported by the GSF file type.
5.2.10 FWrite
Arguments: SVint datagramType
void* data
unsigned char* streamBuf
Returns: SVint
This method is used by decoder that support file writing. Currently, this is only the GSF type.
5.2.11 Seek
Arguments: SVint64 offset
SVint origin (SEEK_BEGIN, SEEK_SET, SEEK_CUR)
Returns: SVint64
This method does a file seek on the underlying sonar file.
5.2.12 TotalPacketTypes
Arguments: None
Returns: SVint
This method returns the total number of packet types for the attached file type.
5.2.13 PacketDefinitions
Arguments: None
Returns: Pio_PacketDef*
This method returns an array of Pio_PacetDef records that contain datagram type and name pairs.
5.2.14 GetSonarType
Arguments: None
Returns: QString
This method will attempt to return a string of the sonar type contained in this file. This method assumes there is only one sonar type.
5.2.15 GetAvailableModes
Arguments: None
Returns: QList<SVint>
This method will return an integer list of available “modes” in the file. Possible modes are defined in Pio_BaseTypes::SonarModeEnum.
5.2.16 GetSystemList
Arguments: None
Returns: QStringList
This method will return a string list of “names” of the systems in the file. This method is only available for internal QPS use.
5.3 PIO_INavMgr
This class interface provides access to navigation interpolation routines. When a Pio_INavMgr object is created from an index file, it will contain all available navigation for the file type. The user can then request navigation information by time stamp. The navigation data will be automatically interpolated according to the passed time stamp.
These objects can also be created from scratch for other purposes.
5.3.1 AddAttrributes
Arguments: SVuint count,
EAttrributeFlags attributeFlags
Returns: bool
This method allocates internal memory to hold “count” instances of the attributes found int the attributeFlag mask. This method is used for manual creation of Pio_INavMgr objects.
5.3.2 Request
Arguments: EAttrributeFlags att
SVdouble t1970,
SVdouble* valArray
Returns: bool
This method requests the specific navigation attribute according to the passed in time stamp. The user must pass the required SVdouble array pointer that will contain the data. For example, if you are requesting EAttributeFlags::RPH data, you will need to bass in a 3-dimensional array.
5.3.3 RequestPosition, RequestHeading, RequestTime, RequestPosPac, RequestAttitudes, RequestTransducerDepth, RequestPlatformDepth, RequestRPH, RequestHeave, RequestTrueHeave, RequestAltitude, RequestRoll, RequestPitch, RequestUser
Arguments: SVdouble t1970,
SVdouble* valArray
Returns: bool
These methods request a specific navigation attribute by name. It behaves the same as the Request(EAttributeFlags…) method.
5.3.4 Add
Arguments: EAttrributeFlags att
SVdouble t1970,
SVdouble* valArray
Returns: bool
This method adds the specific navigation information to the Pio_INavMgr. Be sure to add the data sequentially in time.
5.3.5 AddPosition, AddHeading, AddTime, AddPosPac, AddAttitudes, AddTransducerDepth, AddPlatformDepth, AddRPH, AddHeave, AddTrueHeave, AddAltitude, AddRoll, AddPitch, AddUser
Arguments: SVdouble t1970,
SVdouble* valArray
Returns: bool
These methods add a specific navigation attribute by name. It behaves the same as the Add(EAttributeFlags…) method.
5.3.6 GetExtents (overloaded)
Arguments: SVdouble *vals
Returns: bool
This method returns the xMin, xMax, yMin, yMax positions of the data contained in object.
5.3.7 GetExtents (overloaded)
Arguments: Sv_Extents2D &ext
Returns: bool
This method returns the xMin, xMax, yMin, yMax positions of the data contained in object.
5.3.8 ContainsTime
Arguments: SVdouble
Returns: bool
This method returns true if the time stamp falls within the time of the position navigation data contained in the object.
5.3.9 OverlapsTime
Arguments: SVdouble t0
SVdouble t1
Returns: bool
This method returns true if the time stamps overlap the start/end times of the position navigation data contained in the object.
5.3.10 BoxFilter
Arguments: SVint windowSize
Returns: void
This method runs a smoothing “box-filter” on the arrays of navigation data contained in the object. The box filter window width is passed in as the only argument.
5.3.11 GetAttributeFlags
Arguments: None
Returns: SVuint
This method returns the flag mask for the attributes contained in this navigation manager object.
5.3.12 GetPositionCount
Arguments: None
Returns: SVuint
This method returns number of position fixes in the object.
5.3.13 GetPositionArrays
Arguments: SVdouble *epoch
SVdouble *posX
SVdouble *posY
Returns: bool
This method returns filled arrays of the (time,x,y) data contained in the navigation object. This method is useful when transforming position data contained in the navigation manager.
5.3.14 SetPositionArrays
Arguments: SVdouble *epoch
SVdouble *posX
SVdouble *posY
Returns: bool
This method sets the (time,x,y) data contained in the navigation object. This method is useful when transforming position data contained in the navigation manager.
5.3.15 GetBoundaryTime
Arguments: EAttributeFlags flag
SVdouble *start
SVdouble *stop
Returns: None
This method returns start and stop time for the passed in attribute.
5.3.16 GetCount
Arguments: EAttributeFlags flag
Returns: SVuint
This method returns number of entries for the passed in attribute.
5.3.17 GetAt
Arguments: EAttributeFlags flag
SVuint index,
SVdouble &epoch
SVdouble* valArray
Returns: bool
This method returns a specific attribute entry not by time, but by index. It will return the epoch and values of the attribute.
5.3.18 GetAt
Arguments: EAttributeFlags flag
SVdouble epoch
SVdouble* valArray
Returns: bool
This method returns a specific attribute entry not by index, but by time stamp. It will return the values of the attribute.
5.3.19 GetIndex
Arguments: EAttributeFlags flag
SVdouble epoch
Returns: SVint
This method returns a specific index for the requested attribute at a given timestamp. This will be the index where epoch <= time stamp of a specific attribute entry.
5.3.20 GetNavUnits
Arguments: None
Returns: ENavUnitsEnum
This method returns the navigation units of the internal position data. Only certain formats support this type.
5.3.21 TransformPositions
Arguments: const char * wktIn
const char* wktOut
Returns: void
This method will transform the internal position data to the desired output coordinate system specified by the wktOut parameter.
